Diffusion technique is the most frequently used technique for transistor fabrication. Here, the semiconductor wafer is subjected to gaseous diffusions of both N-type and P-type impurities to form the emitter–base and the collector–base junctions.
Two types of transistors are fabricated using the diffusion technique namely,
• Planar transistors
• Mesa transistors
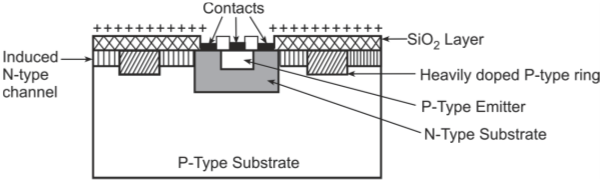
Planar transistor: Planar diffusion NPN Silicon transistor is shown in figure below. The base–collector region is photo-etched on the block of N-type Silicon and a P-type base region is formed by a gaseous diffusion-masking process. The emitter is then diffused onto the base and the whole structure is covered by a layer of Silicon oxide.
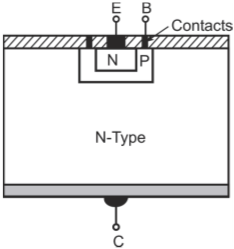
Planar diffusion transistor
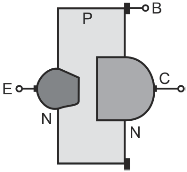
Mesa transistor: It is basically a planar transistor that has been etched at the base–collector junction leaving a mesa or a flat-topped peak as shown in the figure below. These transistors are rugged devices with high power-dissipation capability and can operate at higher frequencies. However, they have higher value of saturation voltage because of highly resistive collector region and are unsuitable for switching applications
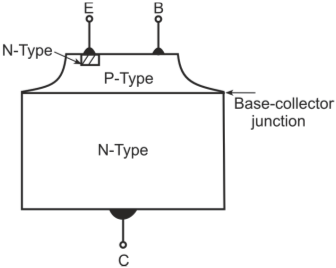
Mesa diffusion transistors