In a dual-gate MOSFET, an additional second insulated gate is provided as compared to a conventional MOSFET. The flow of current through the MOSFET is controlled by voltages at both the gate terminals. Since the control is exerted by two gates, the dual-gate MOSFET may be considered to be the counterpart of a tetrode. Figure below shows the cross-section of an n-channel dual-gate DE-MOSFET.
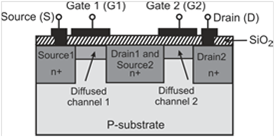
Cross-section of an n-channel dual-gate DE-MOSFET

