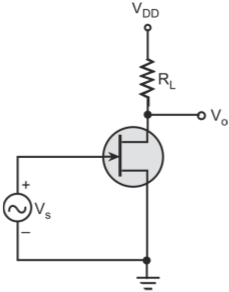
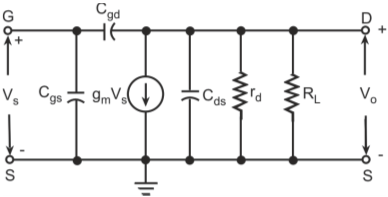
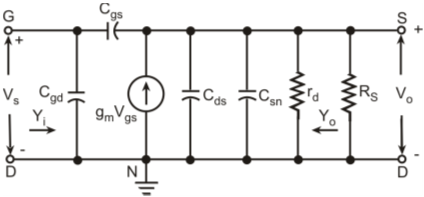
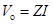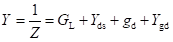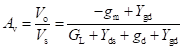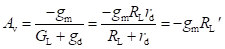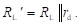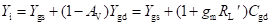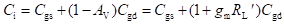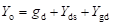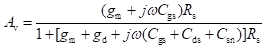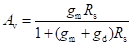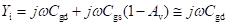High-frequency response of an FET amplifier is similar to that of a BJT amplifier. Figure below shows the high-frequency model for an FET (JFET as well as MOSFET). As we can see from the figure, the high-frequency model is similar to the low-frequency model with the addition of junction capacitances.
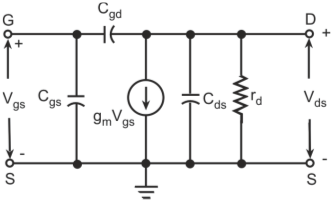
High-frequency model of a FET
The capacitance Cgs represents the barrier capacitance between the gate and the source terminals. Cgd is the barrier capacitance between the gate and the drain terminals. Cds is the drain-to-source capacitance of the channel. These capacitors offer high impedance at lower frequencies and can be considered as open circuit. However, at high frequencies, due to these capacitances feedback exists between the input and output circuits and voltage amplification drops rapidly as the frequency increases.