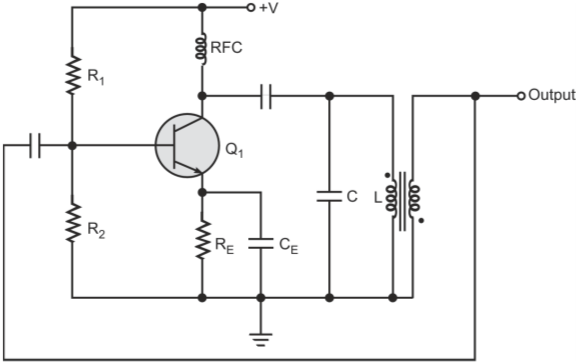
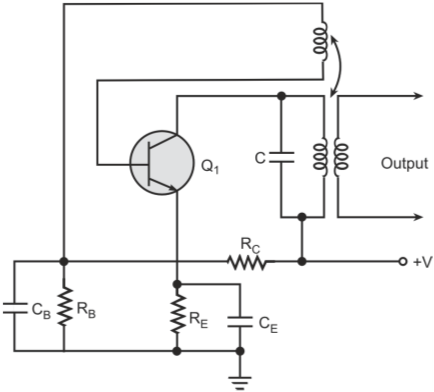
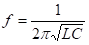Armstrong oscillators, also known as Meissner oscillators, use magnetic coupling as means of feeding part of output signal back to input to provide oscillations.
It is also called a Tickler oscillator due to use of magnetic coupling between the tickler coil and the coupling coil. Tickler coil is the name given to a small coil connected in series with the plate circuit of a vacuum tube and coupled inductively to the grid circuit to provide feedback. In the case of a bipolar junction transistor or an FET, the tickler coil is placed in series with collector or drain circuit and is inductively coupled to the base or gate circuit. A capacitor is placed across either the tickler coil or the coupling coil to form a tank circuit that decides the operating frequency. Figures show the basic circuit arrangements in the two cases with n-channel junction FET used as the active device. Biasing components are omitted for the sake of simplicity.
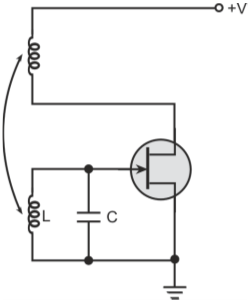
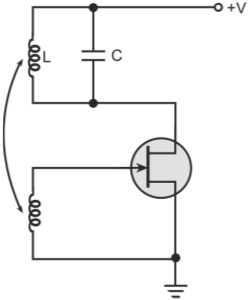
Basic Armstrong oscillator configurations with capacitor across the (a) coupling coil (b) tickler coil