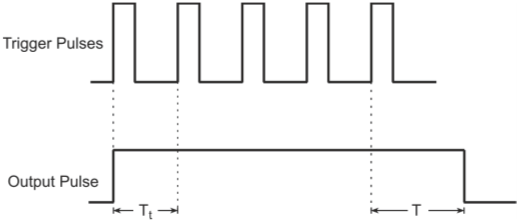
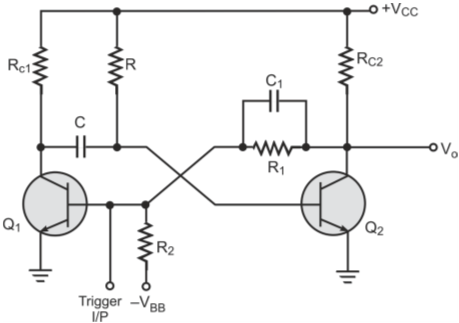
Figure below shows the basic monostable multivibrator circuit.
Monostable multivibrator
The circuit functions as follows.
• Initially, transistor Q2 is in saturation as it gets its base bias from +VCC through R. Coupling from Q2-collector to Q1-base ensures that Q1 is in cut-off.
• When a positive trigger pulse of short duration and sufficient magnitude is applied to the base of transistor Q1, Q1 starts conducting.
• As the voltage across the capacitor C cannot change instantly, negative voltage is applied to the base of transistor Q2 and it turns OFF. Therefore, the output goes to the HIGH state.
• Since there is no direct coupling from Q1-collector to Q2-base, which is necessary for a regenerative process to set in, Q1 is not necessarily in saturation. However, it conducts some current.
• The Q1-collector voltage falls by Ic1Rc1 and Q2-base voltage falls by the same amount as voltage across a capacitor (C in this case) can not change instantaneously.
• In nutshell, the moment trigger is applied, Q2 went to cut-off and Q1 started conducting. But now there is a path for capacitor C to charge from VCC through R and the conducting transistor. The polarity of voltage across C is such that Q2-base potential rises. The moment Q2-base voltage exceeds the cut-in voltage, it turns Q2 ON, which due to coupling through R1 turns Q1 OFF. And we are back to the original state, the stable state.
• Whenever, we trigger the circuit into the other state, it does not stay there permanently and returns back after a time period that depends upon R and C. This state is called the quasi-stable state.